HDR stands for High Dynamic Range which means that it expands the dynamic range of the picture.
It enables the TV to display the content with greater contrast, with more highlights in the bright and dark areas and with better color accuracy.
It helps to display every single nuance of the scene and make the picture more vivid and realistic.
In this article, we are going to have a clear understanding of HDR, how does HDR work on TV and what is the difference between SDR and HDR.
So, without wasting time, let’s dive in.
What is Dynamic Range in TV?
Dynamic range is related to the contrast and color accuracy of the image. These are the two crucial factors on which we can compare the picture quality of TVs.
You must check the contrast ratio of a TV and how realistic colors it can produce before buying one.
These are the things that the salesman may not tell you. He may tell you about the other features like more pixels, better resolution, theatrical sound, better local dimming etc.
But, why I am stressing the two above-mentioned factors, let us understand in detail.
Factors on which HDR depends:
1. Contrast Ratio
The contrast ratio is the ratio of the luminance of the brightest white to the darkest black. The more this ratio, the more distinct the separation between the bright and dark areas.
You will understand it more if you compare two TVs, one with a poor contrast ratio and another with a high contrast ratio, side by side.
You will notice that the blacks in the former TV appear slightly washed out and not so dark. While, in the latter, they appear clear and distinct.
2. Color Accuracy
We have three primary colors; red, blue and green. Using the combination of shades of these primary colors, a billion new colors can be generated.
A TV covers a certain area of the spectrum of colors, which can be ideally generated by using the combinations of different shades of RGB colors. This area is known as the color gamut of the TV.
WCG, or wide colour gamut is often linked with HDR in improving the overall picture quality of the TV. It introduces much more colors to the color palette.
The more accurate shades of color a TV displays, the more lively experience it delivers on the screen.
For example, a premium QLED TV achieves a high contrast ratio through local dimming. It also achieves high color volume and color accuracy by the use of quantum dots.
This combination of high contrast and high color volume will enable it to deliver an excellent HDR performance on the screen.
I think how does HDR work on TV, is slowly becoming clearer to you. Let’s discuss about HDR in detail.
What is HDR in TV?
High Dynamic Range, as the name implies, expands the dynamic range of the picture, i.e., widens the range of the color and contrast of a TV to deliver a more lively experience.
A TV with a high contrast ratio and high color accuracy delivers great HDR performance.
However, not every TV labeled as ‘HDR TV’ performs well. You will find many cheap TVs labeled ‘4K HDR’.
But, if you compare them with an expensive model with the same HDR label, you will notice a tremendous difference in their HDR performance.
For a good HDR performance, high peak brightness, high color accuracy, as well as high contrast ratio, is a must for a TV.
The high contrast ratio combined with high peak brightness helps in the clear distinction of different areas within the scene by making the bright areas even brighter and dark areas even darker.
The color accuracy, on the other hand, makes the reds, blues and greens deeper and brighter, thus bringing out great details on the screen.
What does 4K HDR TV mean? Is it different from a 4K UHD TV?
A 4K Ultra HD TV refers to the 4K resolution which means the TV has 3840×2160 pixels.
A 4K HDR-labelled TV means that the TV is having 4K resolution and also, it can display 4K HDR content.
However, all the HDR-labelled TVs may not display HDR content accurately. Why? We have seen above.
Premium TVs generally have high contrast and color accuracy. Therefore, they can perform very well in HDR.
For example, a premium QLED TV with a large color palette and a fantastic peak brightness performs very well on HDR content.
An OLED TV with a good peak brightness also delivers excellent HDR performance.
This all is true provided that the source is also delivering HDR content.
Only the TV can’t do it without HDR content
An HDR-compatible TV alone can’t perform well in HDR until and unless it plays HDR content. Therefore, the TV must support HDR and the source should also deliver HDR content.
Fortunately, nowadays, HDR content is widely available.
You can find HDR content on many streaming platforms like Netflix and Amazon along with the Ultra HD Blu-rays. In addition, the Playstations and Xbox games also stream HDR content.
Thus, watching HDR content on a true HDR-compatible TV will give you a true HDR experience.
SDR vs HDR
The main difference between SDR (Standard Dynamic Range) and HDR arises based on the number of brightness levels and colors.
While SDR can display a limited number of brightness levels in an image, HDR can display more number of brightness levels in the same image, thus providing more life and depth to the image.
For example, if you can see 5 brightness levels say, 3 nits, 30 nits, 40 nits, 75 nits and 95 nits in an SDR image, then you may see more than 10 brightness levels in the same image when it is mastered in HDR. For example, 0.5 nits, 2 nits, 3 nits, 30 nits, ……, 95 nits, 150 nits,….., 400 nits.
HDR, thus clearly distinguishes the colors and brightness levels as required in different areas of the scene. This causes the highlights to pop and makes the scene more realistic.
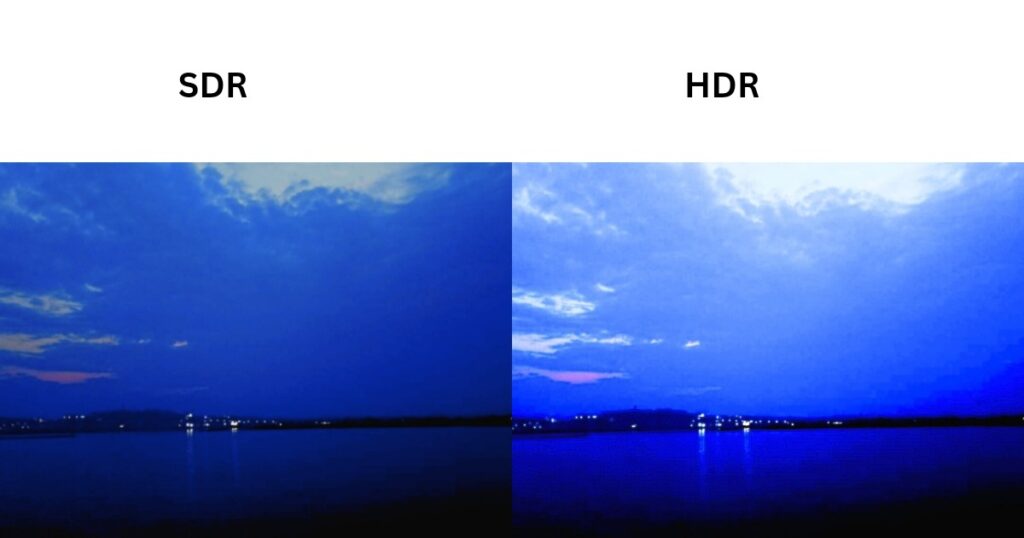

In the above SDR image, you may notice that there is not a large difference in brightness between the brightest and the darkest areas. Moreover, the blacks appear slightly washed out.
But, in the above HDR image, the lights are as bright as close to how much they should be in reality. The blacks are amazing as well and the clouds appear distinctly highlighted in the sky.
There are many more brightness levels in this HDR image with a greater peak brightness. The color tones are better saturated, and each color is shown at the correct brightness as it should be.
These features of HDR bring the image much closer to reality.
TVs with high peak brightness and high contrast ratio can display various brightness levels corresponding to various objects in the scene.
HDR adjusts the brightness levels of various colors depending on which part of the image should appear bright and which one should be dimmed. Thus, the picture appears more appealing as if it is in real life.
This is made possible by the use of metadata in HDR. The metadata is a set of instructions sent by the source delivering the HDR content.
It tells the TV to display the required brightness levels and colors in various parts of the scene accurately.